문장 구조, Sentence Structure (영어 문장 기본 순서)
문장은 완전한 생각을 표현하는 단어들의 그룹이고 주어와 술어를 포함합니다. 가장 기본적인 문장 구조는 주어와 술부로 구성되어 있습니다. 하지만 많은 문장들은 주요한 절과 하나 이상의 하위 절들을 가지고 있습니다.
영어 문장에서 기본 순서는 주어 + 동사 + 목적어입니다. 이것은 단순하게 들리지만, 문장의 구조와 복잡도에 따라 주어, 동사, 그리고 목적어를 구별하는 것은 어려울 수 있습니다. 문장 구조에는 (1) 단문(simple), (2) 중문(compound), (3) 복문(complex), (4) 혼합복문(compound-complex)의 네 가지 유형이 있습니다.
문장의 형태
| 문장 형태 | 문장 구성 | 예시 |
|---|---|---|
| 단문 |
독립절 |
I like animals. |
| 중문 |
독립절+ 등위접속사 (혹은 세미콜론) + 독립절 |
I like animals, but Molly prefers plants. |
| 복문 |
독립절 + 종속접속사 (혹은 관계대명사) + 종속절 |
I like animals because they are cute. |
| 혼합복문 |
독립절 + 종속접속사 + 종속절 + 등위접속사 + 독립절 |
I like animals because they are cute, so I work at an animal shelter. |
학술적 글쓰기에서 영어 문장 구조
단문 구조
단문은 가장 기본적인 문장 구조이고 하나의 독립된 절로 구성되어 있습니다.
절의 종류
독립절은 완전한 사고를 표현합니다. 독립절만이 온전한 문장으로 기능할 수 있습니다.
- 예시
- The proposed system has the advantage of a wide scope.
I went shopping last weekend.
The cat is sleeping by the window.
반면에, 종속절은 완전한 사고를 표현하지 않으며 온전한 문장으로 기능할 수 없습니다.
- 예시
- which was developed over three months
even though I was tired
because the weather is sunny
흔히 쓰이는 종속접속사
because, since, once, although, if, until, unless, why, while, whether, than, that, in order to
흔히 쓰이는 관계대명사
that, which, who, whom, whoever, whomever
문장의 주어
주어는 문장의 동작을 수행하는 어떤 것이든 될 수 있습니다. 주어는 문장의 두 가지 기본 요소 중 첫 번째입니다.
- 예시
- This study investigated the relationship between the personal traits and clinical parameters.
- 예시
- Dolly made a cake for the party.
문장의 술부
술부는 주어의 동사(동작)을 포함하며 추가적인 정보를 전달할 수 있습니다.
- 예시
- This study investigated the relationship between the personal traits and clinical parameters.
- 예시
- Mary gave her sheep a bath.
직접 및 간접 목적어
직접 목적어는 동작을 받는 사람이나 물건 혹은 견해입니다.
- 예시
- This study investigated the relationship between the personal traits and clinical parameters.
- 예시
- Dolly made a cake.
간접 목적어는 동작이 적용된 사람이나 물건 혹은 견해를 말합니다.
- 예시
- The national lab offered us an opportunity to work on an exciting new project.
- 예시
- Mary gave her sheep a bath.
타동사 vs. 자동사
타동사는 주어가 직접 목적어에 대해 취하는 행동입니다.
- 예시
- We fabricated a composite.
여기서, "we"는 주어이고, "fabricated"은 타동사이고, "a composite"은 직접 목적어입니다.
자동사는 목적어가 뒤따라올 필요가 없는 동사입니다. 자동사는 스스로 술어로 기능할 수 있습니다.
- 예시
- We arrived.
We arrived early.
- 예시
- I always eat.
I always eat before work.
“We” 와 “I” 는 주어고; “arrived” 와 “eat” 는 자동사입니다.
주격보어
주격보어는 주어에 다른 이름을 부여하거나 설명하여 보완합니다. 주격보완은 항상 연결 동사를 따르는데, 이것은 종종 동사 "to be"의 형태입니다.
- 예시
- The material is a gold composite.
“Gold composite” 은 “the material” 의 다른 이름입니다.
- 예시
- Charlotte is very pretty.
“Pretty” 는 주어 “Charlotte” 을 설명합니다.
지금 원어민 전문 에디터의 영문 교정을 통해서 첨삭 피드백을 받아보세요!
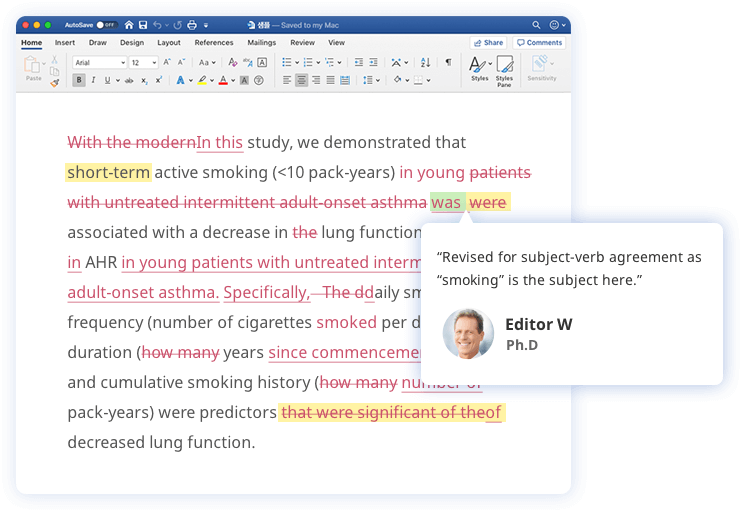
- 학술논문
- 유학지원서
- 취업지원서
- 사업 리포트
- 블로그 웹사이트
- 수필 및 개인적인 글
중문 구조
중문은 두 개 이상의 독립 절이 등위접속사나 세미콜론으로 연결됩니다. 미국 영어 규칙에서 독립절들을 연결할 때는 반드시 등위접속사가 쉼표와 함께 사용되어야 합니다.
중문 구조 : 독립절 + 등위접속사 (혹은 세미콜론) + 독립절
등위접속사 예시 : and, but, yet, or, nor, for, so
- 예시
- The material is a gold composite, and it was fabricated in clean room no. 45.
- 예시
- Glenda usually eats before work, but today she could not.
- 예시
- The proposed system has the advantage of a wide scope; it uses a novel algorithm that expands the range by a factor of ten.
복문 구조
복문 구조복문은 독립절과 종속절로 구성되어 있습니다.
복문 구조 : 독립절 + 종속접속사 (혹은 관계대명사) + 종속절
- 예시
- We built a new system because the previous model had to be narrowed in scope.
- 예시
- Sarah will buy a train ticket if her flight is cancelled.
혼합복문 구조
혼합복문은 둘 이상의 독립절과 하나 이상의 종속절로 구성됩니다.
혼합복문 구조 : 독립절 + 종속접속사 + 종속절 + 등위접속사 + 독립절
- 예시
- The first method failed because it caused the wires to melt, but the second method succeeded in bending the wires without causing the same issue.
- 예시
- Sarah’s flight took off before she started driving to the airport, so she drove to the train station instead.
문장 구조의 정확성을 높이기 위해, 작성한 후 문장 검사기를 활용하여 문법적 오류를 점검하는 것이 좋습니다. 이러한 도구를 사용하면 문장 구조의 오류를 효과적으로 찾아내고 수정할 수 있습니다.

